|
CEE 772 |
16 November 2005 |
Mid-term Exam
Open Book, Open Notes
Answer any two of the following six questions:
(each
is worth 50%)
1. Sample Preparation
A 1-liter aqueous sample is being extracted in a
sequential batch mode with methyl-tertiary-butyl ether (MtBE). Pollutant "Y" has an MtBE/water dimensionless partition coefficient of 25.
a.
After one extraction with 50 mL of MtBE, how much of the original amount of pollutant
"Y" remains in the water phase?
b.
What is the overall % of pollutant "Y" that would be extracted into
the MtBE phase if 5 sequential extractions using 50 mL of the organic phase were made?
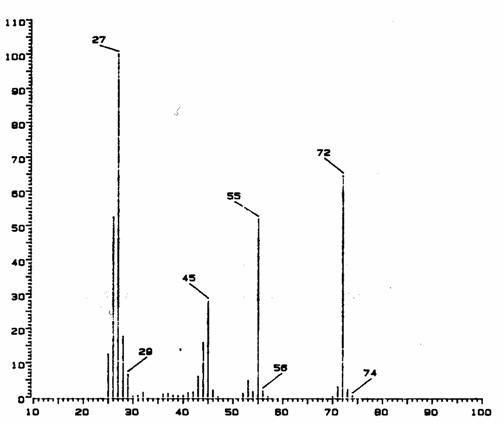
2. GC/MS #1
Interpret the mass spectrum depicted in the
figure below. Indicate your rationale
for the determination of empirical formulae for each of the major fragment
ions, as well as for the molecular ion.
Propose a structure for the parent molecule.

3. GC/MS #2
Interpret the mass spectrum depicted in the
figure below. Indicate your rationale
for the determination of empirical formulae for each of the major fragment
ions, as well as for the molecular ion.
Propose a structure for the parent molecule.
4. Error Analysis
A series of replicate measurements were made for
dichloracetamide in identical aliquots of a drinking
water sample. The measurements are as
follows:
|
0.35 µg/L |
0.39 µg/L |
0.52 µg/L |
|
0.44 µg/L |
0.40 µg/L |
0.41 µg/L |
a. What is the mean and relative standard deviation
for these measurements?
b. If these measurement represent concentrations
near the method detection limit (MDL), what would you calculated the MDL to be?
c. Calculate a 95% confidence interval for the mean
of these measurements.
5. General
Answer each of the following as either true (T)
or false (F).
a.
Atomic absorption spectrophotometry
relies on line sources of light
b.
Diode array spectrophotometers use filters
instead of monochromators for wavelength selection
c.
One important type of sample preparation in
gas chromatography is derivatization, which results
in chemical changes in the analytes
d.
Stray light will result in abnormally high
absorbance readings with double-beam instruments
e.
High levels of sample absorbance can
interfere with TOC analysis
f.
TOX analyzers can measure organic chlorine,
organic bromine, organic iodine, but not organic fluorine
g.
Most gas chromatographic detectors use light
absorption for detection of compounds leaving the GC column.
h.
Flame Atomic absorption spectrophotometry
is enhanced by use of an L’vov platform
i. Chromatographic separations generally improve
as particle size, or film thickness decreases
j.
Sample preparation in atomic absorption spectrophotometry frequently involves addition of matrix
modifiers, which can help avoid interferents.
6. TOC
Explain how you would measure TOC in
gasoline-contaminated groundwater.
Consider matrix problems, interferents, analyte recovery and any other pertinent issues. Be as specific as you can. How could one best verify the accuracy of
this method?
|
m/e
|
%
Abundance |
m/e
|
%
Abundance |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|