|
CEE 370 |
Spring 2001 |
Exam #1
March 15, 2001
Closed Book, one sheet of notes allowed
Please answer any 5 of the following 13 questions. Each is worth 20 points. Show all work. Be neat, and box-in your answer.
1. Calculate the ThOD of the following wastewaters in mg/L: (20 points)
a. 10-3 moles/L of dodecane, C12H26
The balanced stoichiometric equation is:
![]()
The ThOD is then:
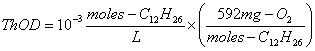
![]()
b. 3x10-3 moles/L of oxalic acid, C2H2O4
The balanced stoichiometric equation is:
![]()
The ThOD is then:
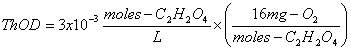
![]()
2. Calculate the concentration of the following solutions as mg-Carbon/L and tell which family of organic compounds each comes from: (20 points)
a. 10-3 moles/L of hexane, C6H8
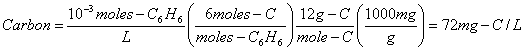
Hexane is a member of the Alkane family.
b. 3x10-3 moles/L of oxalic acid, C2H2O4
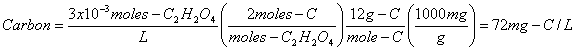
Oxalic Acid is a member of the Carboxylic Acid family.
c. 30 mg-ethanol/L, CH3CH2OH
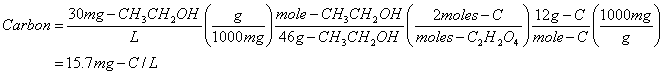
Ethanol is a member of the Alcohol family.
3. Short Answer (20 points)
a. What distinguishes a carboxylic acid from other chemical substances? (5 points)
- COOH groups
- Donate protons to water
b. Explain what pseudo first order means. (5 points)
Due to an excess of one or more reactants, the reaction rate is proportional to the concentration of only one of the reactants
c. Why does ozone form in the upper atmosphere? (5 points)
Light of low wavelength (thus, high energy) strikes oxygen in the upper atmosphere to form ozone. This high energy light does not substantially penetrate into the lower atmosphere.
d. What is the difference between partitioning and adsorption? (5 points)
Partitioning occurs where a pollutant separates from the dissolved state to a state where it is associated with a particle or solid surface. The nature of this association may be either a direct link to the solid surface (adsorption) or dissolution into an organic layer attached to the surface.
4. Perform a charge balance on the following water. As part of this balance determine the amount of unbalanced charge and its percentage of the total. What does this number tell you about the accuracy of the chemical analysis? (20 points)
|
Chemical Substance |
Conc. (mg/L) |
GFW |
Conc. (mM) |
Conc. (meq/L) |
|
Na+ |
31.2 |
22.9898 |
1.3571236 |
1.3571236 |
|
K+ |
1.5 |
39.0983 |
0.0383648 |
0.0383648 |
|
Ca+2 |
42.8 |
40.08 |
1.0678643 |
2.1357285 |
|
Mg+2 |
3.5 |
24.305 |
0.1440033 |
0.2880066 |
|
NO3- |
8.8 |
62.0049 |
0.1419243 |
0.1419243 |
|
SO4-2 |
14.6 |
96.0576 |
0.1519921 |
0.3039843 |
|
Cl- |
37.2 |
35.453 |
1.0492765 |
1.0492765 |
|
HCO3- |
59.3 |
61.0171 |
0.9718587 |
0.9718587 |
|
cations = |
3.81922356 |
|
anions = |
2.46704376 |
|
|
|
|
% diff. =
|
35.40% |
This tells us that there is a substantial error. Either the cations are over estimated, the anions are underestimated or there is a major anion that was omitted.
5. What is the TDS (in mg/L), the total hardness (in mg/L as CaCO3) and the total alkalinity (in mg/L as CaCO3) for the water in question #4? (20 points)
|
|
Chemical
Substance |
Conc. (mg/L) |
|
|
Na+ |
31.2 |
|
|
K+ |
1.5 |
|
|
Ca+2 |
42.8 |
|
|
Mg+2 |
3.5 |
|
|
NO3- |
8.8 |
|
|
SO4-2 |
14.6 |
|
|
Cl- |
37.2 |
|
|
HCO3- |
59.3 |
|
|
Sum = |
198.9 |
mg/L |
|
|
or |
Sum = |
139.6 |
mg/L |
with loss
of CO2 |
6. What is the ionic strength for the water in question #4? (20 points)
|
Chemical
Substance |
Conc. (mg/L) |
GFW |
Conc. (mM) |
Conc. (meq/L) |
z |
z^2 |
cz^2 (M) |
|
Na+ |
31.2 |
22.9898 |
1.3571236 |
1.3571236 |
1 |
1 |
0.001357 |
|
K+ |
1.5 |
39.0983 |
0.0383648 |
0.0383648 |
1 |
1 |
3.84E-05 |
|
Ca+2 |
42.8 |
40.08 |
1.0678643 |
2.1357285 |
2 |
4 |
0.004271 |
|
Mg+2 |
3.5 |
24.305 |
0.1440033 |
0.2880066 |
2 |
4 |
0.000576 |
|
NO3- |
8.8 |
62.0049 |
0.1419243 |
0.1419243 |
1 |
1 |
0.000142 |
|
SO4-2 |
14.6 |
96.0576 |
0.1519921 |
0.3039843 |
2 |
4 |
0.000608 |
|
Cl- |
37.2 |
35.453 |
1.0492765 |
1.0492765 |
1 |
1 |
0.001049 |
|
HCO3- |
59.3 |
61.0171 |
0.9718587 |
0.9718587 |
1 |
1 |
0.000972 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.5*Sum = |
0.004507 |
7. Determine the TDS value in mg/L based on the following analysis. Four hundred milliliters of a water sample are filtered though a glass fiber filter. The filter paper is dried to a constant weight (1.4569 g). Two hundred fifty milliliters of the filtrate are added to an evaporating dish. The tare for this dish was 24.5087 g. The dish and water are placed in a drying oven and removed after all of the water is gone. Once it has returned to room temperature, the dish is re-weighed and found to be 24.8904 g. (20 points)
![]()
8. True/False. Indicate whether the following statements are true (T) or false (F). (20 points total; 2 points each)
|
1. |
T |
A 1N
concentration is the same as 1 equivalent/L |
|
2. |
F |
A water
having 100 mg/L of hardness as CaCO3 may also be said to have 10
moles/L of hardness |
|
3. |
T |
The
activity coefficient usually goes down as ionic strength goes up. |
|
4. |
F |
A first
order reaction is almost always slower that a second order reaction |
|
5. |
T |
Catalysts
accelerate chemical reactions by lowering the activation energy |
|
6. |
F |
When Gibbs
Free Energy increases, the reaction will tend to go forward |
|
7. |
F |
Alkenes all
have triple bonds |
|
8. |
T |
Henry’s law
describes the relationship between partial pressure and dissolved
concentration |
|
9. |
T |
As the
organic content of a sediment increases, its ability to accumulate organic
contaminants by partitioning increases |
|
10. |
F |
TSS is
always greater than TDS |
9. Use the following data to estimate the rate constant for the reaction between A and B at 40°C (20 points)
|
Temperature |
Rate constant |
|
20°C |
3.6 M-1s-1 |
|
50°C |
56.2 M-1s-1 |
Best to use the Arrhenius Equation:
![]()
so then:
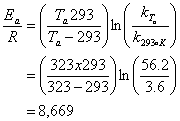
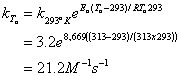
10. The half life for toluene in groundwater is estimated to be 12 days. If the concentration of toluene in a groundwater plume is currently 48 ppb, what will the concentration be 30 days from now? (20 points)
![]()
so:
![]()
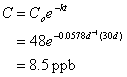
11. The equilibrium constant for the following reaction is 10-12.3. What percent of the total phosphate is in the form of HPO4-2 at pH 13? (20 points)
HPO4-2 = PO4-3 + H+
![]()
![]()
![]()
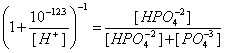
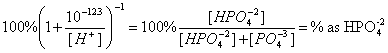
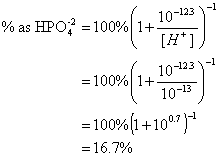
12. You’ve added 10-4 moles of sodium carbonate to a liter of water. List all possible species and write the necessary equations (equilibrium, mass balance, electroneutrality) to solve this chemical system (20 points)
Species:
- Na+
- CO3-2
- HCO3-
- H2CO3
- H+
- OH-
Equations:
- Kw=[OH-][H+]
- K1 = [H+][HCO3-]/[ H2CO3]
- K2 = [H+][CO3-2]/[ HCO3-]
- Ct = [Na+] = [H2CO3] + [HCO3-] + [CO3-2]
- [Na+] + [H+] = [HCO3-] + 2[CO3-2]
13. You need to oxidize nitrite (NO2-) to nitrate (NO3-) by addition of potassium permanganate (KMnO4). After the reaction is complete, the manganese is reduced to manganese dioxide (MnO2). How many mg/L of permanganate are needed to completely oxidize 4.6 mg/L of nitrite? (20 points).
First, you must balance the REDOX equation to get the stoichiometry. This requires that the oxidation states for N and Mn be determined, and the electrons be balanced, then balance all non-H/O atoms, finally balance the O atoms with water as needed, and the H with the proton as needed.
![]()
now calculate:
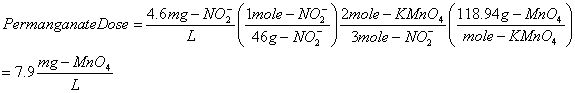
Appendix
Selected Chemical Constants
|
Element |
Symbol |
Atomic # |
Atomic Wt. |
Valence |
Electronegativity |
|
|
Aluminum |
Al |
13 |
26.98 |
3 |
1.47 |
|
|
Boron |
B |
5 |
10.81 |
3 |
2.01 |
|
|
Calcium |
Ca |
20 |
40.08 |
2 |
1.04 |
|
|
Carbon |
C |
6 |
12.01 |
2,4 |
2.50 |
|
|
Cerium |
Ce |
58 |
140.12 |
3,4 |
1.06 |
|
|
Helium |
He |
2 |
4.00 |
0 |
|
|
|
Holmiuum |
Ho |
67 |
164.93 |
3 |
1.10 |
|
|
Hydrogen |
H |
1 |
1.01 |
1 |
2.20 |
|
|
Magnesium |
Mg |
12 |
24.31 |
2 |
1.23 |
|
|
Manganese |
Mn |
25 |
54.94 |
2,3,4,6,7 |
1.60 |
|
|
Osmium |
Os |
76 |
190.2 |
2,3,4,8 |
1.52 |
|
|
Oxygen |
O |
8 |
16.00 |
2 |
3.50 |
|
|
Potassium |
K |
19 |
39.10 |
1 |
0.91 |
|
|
Sodium |
Na |
11 |
22.99 |
1 |
1.01 |
|
|
Sulfur |
S |
16 |
32.06 |
2,4,6 |
2.44 |
|
Selected Acidity Constants (Aqueous Solution, 25°C, I = 0)
|
NAME |
FORMULA |
pKa |
|
|
Hydrochloric acid |
HCl = H+ + Cl- |
-3 |
|
|
Sulfuric acid |
H2SO4= H+ + HSO4- |
-3 (&2) ACIDS |
|
|
Nitric acid |
HNO3 = H+ + NO3- |
-0 |
|
|
Hydronium ion |
H3O+ = H+ + H2O |
0 |
|
|
Bisulfate ion |
HSO4- = H+ +
SO4-2 |
2 |
|
|
Phosphoric acid |
H3PO4 = H+ + H2PO4- |
2.15 (&7.2,12.3) |
|
|
Hydrofluoric acid |
HF = H+
+ F- |
3.2 |
|
|
Nitrous acid |
HNO2 = H+ + NO2- |
4.5 |
|
|
Acetic acid |
CH3COOH = H+ + CH3COO- |
4.75 |
|
|
Propionic acid |
C2H5COOH = H+ + C2H5COO- |
4.87 |
|
|
Carbonic acid |
H2CO3 = H+ + HCO3- |
6.35 (&10.33) |
|
|
Hydrogen sulfide |
H2S = H+ + HS- |
7.02 (&13.9) |
|
|
Dihydrogen phosphate |
H2PO4- = H+ + HPO4-2 |
7.2 |
|
|
Hypochlorous acid |
HOCl = H+
+ OCl- |
7.5 |
|
|
Ammonium ion |
NH4+ = H+ + NH3 |
9.24 |
|
|
Hydrocyanic acid |
HCN = H+
+ CN- |
9.3 |
|
|
Phenol |
C6H5OH = H+ + C6H5O- |
9.9 |
|
|
Bicarbonate ion |
HCO3- = H+ + CO3-2 |
10.33 |
|
|
Monohydrogen phosphate |
HPO4-2 = H+ + PO4-3 |
12.3 |
|
|
Bisulfide ion |
HS- = H+ + S-2 |
13.9 |
|
|
Water |
H2O = H+ + OH- |
14.00 |
|