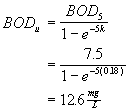
|
CEE 370 |
Spring 1997 |
Exam #2
April 15, 1997
Closed book, 2 sheets of notes allowed.
Please answer all of questions #1 through #5 and one of either #6 or #7. Show all work. Be neat, and box-in your answer.
Answer #1-#5
The Northampton wastewater treatment plant discharges 4.5 MGD of treated wastewater with a BOD5 of 7.5 mg/L. What is the loading in lb of ultimate BOD per day (i.e., lb-BODu/d). Assume a BOD rate constant (k) of 0.18 d-1.
Solution to #1
First calculate the ultimate BOD in the effluent
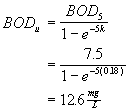
then multiply this by the flow with the appropriate conversion factor.
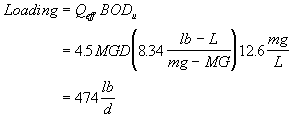
You have designed a batch diffused aeration system for transferring oxygen into a groundwater. The tank holds 5000 gal, and it has a gas transfer coefficient (KLa) of 0.12 min-1. If the raw groundwater has a DO of 1.5 mg/L and the treated water must have a DO of 7.5 mg/L how may gallons per day can be treated by this system? Assume that the saturation value (Cs) is 10.2 mg/L. Ignore the time required to fill and drain the tank.
Solution to #2
First calculate the time required to process one batch of 5000 gal.
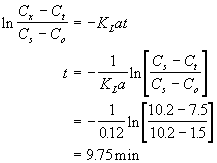
Now calculate the number of batches per day and the total volume treated:
# batches = 24hrs(60min)/9.75min = 147.7
Volume treated = 147.7 batches/day * 5000 gal/batch
= 738,000 gal/day
= 0.74 MGD
A conventional water treatment plant is to be constructed to process 185,000 m3/d. Pilot-plant analysis indicates that an overflow rate of 5 m/hr will be acceptable in the gravity settling tanks. Assuming a surface configuration of approximately 12x30 m, how many settling tanks will be required? Allow one unit out of service for cleaning.
Solution to #3
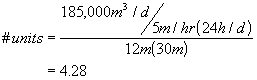
Thus, a minimum of 5 settling tanks are needed, and allowing 1 to be continually out of service for backwash, means that 6 tanks are required.
How many mg/L of hypochlorous acid are required to oxidize 0.8 mg/L ferrous iron?
Solution to #4
First balance the equation:
![]()
Next calculate the mass requirements
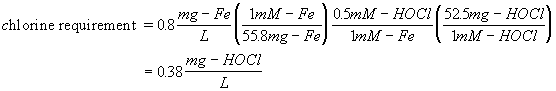
Since most forms of chlorine are expressed as Cl2, the more accepted answer would be:
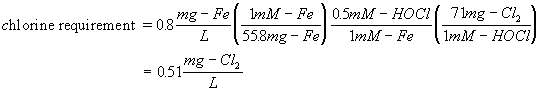
Answer to a:
Total hardness: sum of calcium and magnesium concentration in a water
Carbonate hardness: portion of the total hardness that is matched by the anions, carbonate and bicarbonate
Answer to b:
The product of concentration (C ) times time (t) that gives a certain degree of kill of a given organisms with a specific disinfectant.
Answer to c:
Includes rapid mix, coagulation, flocculation, settling, filtration.
Non-conventional processes may include, GAC adsorption, biological filtration, flotation, membrane processes, intermediate ozonation.
Answer either #6 or #7
A settling tank has a width of 20 ft, a depth of 10 ft and a length of 60 ft. It receives 0.60 ft3/s of flow. What fraction of all 0.10 mm diameter alum floc particles will be removed at 5oC (assume 1.04 g/mL floc density)?
Solution to 6:
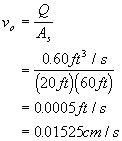
![]()
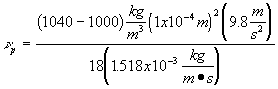
![]()
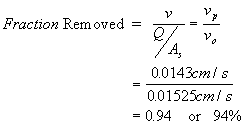
The Intercontinental Paper Co. is discharging its wastewater directly into the Mill River. The discharge flow is 3.8 ft3/s (cfs) the discharge D.O. is 8.5 mg/L and the discharge ultimate BOD (BODu) is 35 mg/L. They obtain half of this water from an intake 0.5 miles upstream of the wastewater outfall, and half from groundwater via a nearby well field. On average, the Mill River water upstream of the IPC outfall has an ultimate BOD (BODu) of 2.5 mg/L and a D.O. of 8.5 mg/L. If the Mill River has a flow of 12 cfs upstream of the IPC intake, and if the state permits a minimum DO of 7.5 mg/L in the Mill River, will the state have to further restrict the BOD in IPC's wastewater (i.e., is the stream out of compliance)? Calculate the minimum stream D.O. expected as a result of the IPC discharge.
Additional assumptions: BOD deoxygenation rate: k1 = 0.23 d-1
reaeration rate constant (k2) of 0.82 d-1
D.O saturation concentration = 9.5 mg/L
River flow velocity = 0.5 ft/s
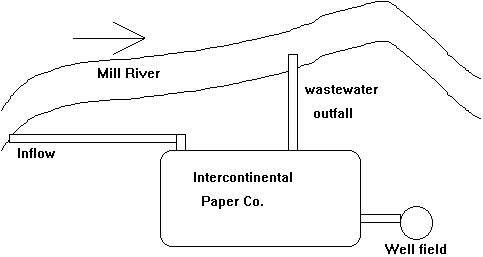
Solution to #7
First the downstream flow is:
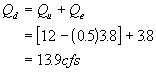
The solve for the in-stream BODu concentration at the point of discharge using a mass balance:
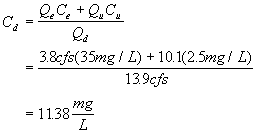
Now determine the critical travel time:
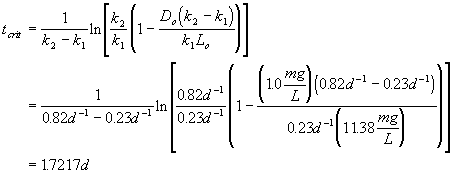
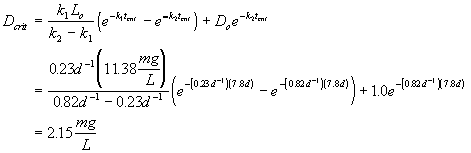
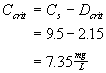
Yes, the stream will be out of compliance.
Appendix
Some physical constants of Water:
|
Temp., oC |
Density, kg/m3 |
Viscosity, N-s/m2 |
Kinematic Viscosity, m2/s |
|
0 |
999.8 |
1.781x10-3 |
1.785x10-6 |
|
5 |
1000.0 |
1.518 x10-3 |
1.519x10-6 |
|
10 |
999.7 |
1.307 x10-3 |
1.306 x10-6 |
|
15 |
999.1 |
1.139 x10-3 |
1.139 x10-6 |
|
20 |
998.2 |
1.002 x10-3 |
1.003 x10-6 |
|
25 |
997.0 |
0.890 x10-3 |
0.893 x10-6 |
|
30 |
995.7 |
0.798 x10-3 |
0.800 x10-6 |
|
35 |
994.0 |
0.725 x10-3 |
0.729 x10-6 |
|
40 |
992.2 |
0.653 x10-3 |
0.658 x10-6 |
Selected Chemical Constants
|
Element |
Symbol |
Atomic # |
Atomic Wt. |
Valence |
Electronegativity |
|
|
Aluminum |
Al |
13 |
26.98 |
3 |
1.47 |
|
|
Boron |
B |
5 |
10.81 |
3 |
2.01 |
|
|
Calcium |
Ca |
20 |
40.08 |
2 |
1.04 |
|
|
Carbon |
C |
6 |
12.01 |
2,4 |
2.50 |
|
|
Cerium |
Ce |
58 |
140.12 |
3,4 |
1.06 |
|
|
Chlorine |
Cl |
17 |
35.453 |
1 |
||
|
Holmiuum |
Ho |
67 |
164.93 |
3 |
1.10 |
|
|
Hydrogen |
H |
1 |
1.01 |
1 |
2.20 |
|
|
Magnesium |
Mg |
12 |
24.31 |
2 |
1.23 |
|
|
Manganese |
Mn |
25 |
54.94 |
2,3,4,6,7 |
1.60 |
|
|
Osmium |
Os |
76 |
190.2 |
2,3,4,8 |
1.52 |
|
|
Oxygen |
O |
8 |
16.00 |
2 |
3.50 |
|
|
Potassium |
K |
19 |
39.10 |
1 |
0.91 |
|
|
Sodium |
Na |
11 |
22.99 |
1 |
1.01 |
|
|
Sulfur |
S |
16 |
32.06 |
2,4,6 |
2.44 |
|
Useful conversion factors
![]()
![]()
![]()
1 ft = 0.305 m